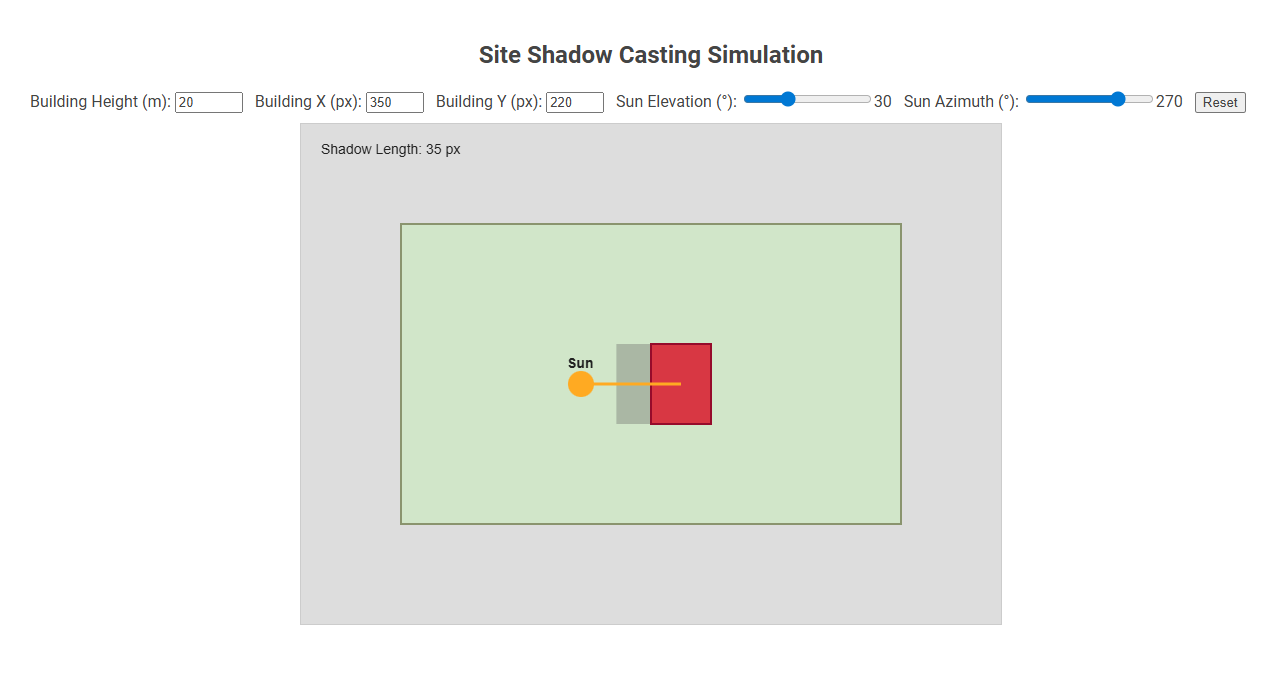
The Site Shadow Casting Simulation tool dynamically visualizes how a building's shadow changes based on building height, position, and real-time sun angle adjustments. It helps architects, urban planners, and engineers optimize building placement and design by analyzing potential shadow impacts on a site. Users input building and sunlight parameters to instantly simulate shadow length and direction for effective site planning.
How to use this tool?
Complete Guide: Site Shadow Casting Simulation Tool
-
Understanding the User Interface:
- Building Height (m): Enter the height of your building in meters.
- Building X (px), Building Y (px): Adjust the horizontal (X) and vertical (Y) position of the building on the simulation canvas in pixels.
- Sun Elevation (deg): Use the slider to select the sun's elevation angle (height of the sun above the ground/skyline) in degrees.
- Sun Azimuth (deg): Use the slider to rotate the sun's position around the building. Azimuth defines the sun's compass direction.
- Reset Button: Click to return all values to their default settings.
-
Setting Simulation Parameters:
- Input the Building Height to simulate different building elevations and observe the effect on shadow length and direction.
- Adjust Building X and Y values to position the building anywhere on the site diagram.
- Modify Sun Elevation using the slider. Lower angles (morning/evening) yield longer shadows, higher angles (noon) create shorter shadows.
- Change the Sun Azimuth slider to see how the shadow's direction rotates around the building based on compass orientation.
-
Interpreting the Visualization:
- The red square represents your building.
- The yellow circle is the sun's current position.
- The shadow appears as a translucent gray rectangle extending from the building, showing the shadow cast based on current sun conditions.
- The shadow length is calculated and displayed in pixels. Longer shadows indicate lower sun elevations.
-
Experimenting and Resetting:
- Try different building positions and sun angles to study how site layout and time/season might influence shadowing for your project.
- Click Reset to quickly start over or compare multiple scenarios.
-
Applications:
- Use the tool to optimize building placement, identify potential overshadowing issues, plan for solar access, or evaluate seasonal solar paths.
Introduction to Free Architectural Shadow Casting Tools
Site shadow casting simulation enhances architectural design by accurately predicting sunlight and shading effects. Free tools like Shadow Analysis by SketchUp, SunCalc, and Heliodon provide accessible options for modeling shadows based on geographic location and time. These tools support sustainable design by optimizing natural light and reducing energy consumption.
Key Features of Online Shadow Simulation Platforms
Site shadow casting simulation platforms offer precise analysis of sun patterns and shadow impact on your property throughout the day and year. Key features include 3D modeling, real-time sunlight tracking, and customizable settings for accurate environment replication. These tools help you optimize structure placement and improve energy efficiency by visualizing potential shading scenarios.
Step-by-Step Setup: Inputting Building and Site Data
Site shadow casting simulation begins with inputting accurate building dimensions and precise geographic coordinates to ensure realistic shadow analysis. You enter detailed site data including topography, surrounding structures, and sun path information to model shadow patterns accurately. This step-by-step setup is essential for predicting shadow impacts and optimizing building placement.
Manipulating Sun Position: Elevation and Azimuth Explained
Site shadow casting simulation enhances your design precision by manipulating sun position through elevation and azimuth angles. Elevation measures the sun's height above the horizon, impacting shadow length and intensity throughout the day. Azimuth defines the sun's horizontal direction, allowing accurate prediction of shadow direction for optimal site planning.
Real-Time Visualization: Deciphering Shadows and Output
Site shadow casting simulation leverages advanced algorithms to generate real-time visualization of shadows, enhancing spatial awareness and design accuracy. High-performance GPUs process dynamic lighting and occlusion data, enabling precise shadow mapping and interactive output adjustments. This technology supports architects and planners in optimizing site layouts by revealing shadow impacts throughout different times of day and seasons.
Customizing Simulations for Site-Specific Contexts
Site shadow casting simulation tailors analyses to unique geographic, architectural, and environmental conditions, enhancing accuracy for urban planning and renewable energy projects. Customizing simulations involves integrating site-specific data such as sun path, local topography, and building geometry to predict precise shadow impacts throughout the year. This targeted approach improves decision-making for optimizing solar panel placement, minimizing shading conflicts, and maximizing site usability.
Practical Applications in Architecture and Urban Planning
Site shadow casting simulation enhances architectural design by accurately predicting sunlight exposure and shading on buildings throughout the day and year. Your projects benefit from optimized natural light usage, improved energy efficiency, and compliance with zoning regulations in urban planning. These simulations support informed decisions for comfortable, sustainable, and visually appealing environments.
Troubleshooting Common User Challenges
Site shadow casting simulation often encounters issues like inaccurate shadow placement, runtime errors, and performance slowdowns. Users should verify correct geolocation settings, ensure the model's geometry is well-defined, and update simulation software to the latest version. Optimizing mesh quality and validating light source parameters significantly improve accuracy and reduce troubleshooting time.
Comparing Free Tools: Accuracy and Usability Insights
Site shadow casting simulation plays a crucial role in urban planning and solar analysis by predicting shading impacts on structures and landscapes. Comparing free tools like SolTrace, SketchUp with Shadow Analysis, and Heliodon reveals varying levels of accuracy influenced by algorithm complexity and geographic data integration. Usability insights highlight SketchUp's intuitive interface for beginners, while SolTrace offers advanced precision for solar engineers, emphasizing the trade-off between ease of use and simulation detail.
Site shadow casting simulation Tool Preview